Pay Less Attention with Lightweight and Dynamic Convolutions
Dynamic convolution은 position-based attention이다.
- Depthwise convolution 기반으로,
- 일부 채널의 weight를 공유하고 (lightweight),
- 타임스텝마다 서로 다른 컨볼루션 커널을 학습하여 (dynamic)
파라미터 수와 시퀀스 길이 대비 계산복잡도를 줄였다. 현재 NLP에서 주류를 차지하는 content-based self-attention이 필수적이지 않다는 것을 보인 데 의미가 있다.
배경 지식
Self-attention
$\mathrm{Attention}(Q, K, V) = \mathrm{softmax}(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}})V$
Content-based attention으로, $Q$ (현재 타임스텝)과, $K$ (context의 다른 모든 요소들)의 scaled & normalized dot-product를 weight로 하여 weighted sum을 구한다. Multihead를 사용하여 각 헤드가 서로 다른 위치를 attend하고, $d_k$개의 feature에 걸쳐 서로 다른 attention weight을 학습할 수 있다.
Context size에 대한 제한은 이론적으로 없으나, 현실적으로 long-range dependency를 계산하는 데 무리가 있다. 인풋 시퀀스 대비 복잡도가 $O(N^2)$이기 때문이다 (N개의 요소를 보는 계산을 총 N번 해야 함).
Depthwise separable convolution
Temporal dimension이 $k$이고, $d$개의 channel이 있는 1D convolution 기준으로 생각하자.
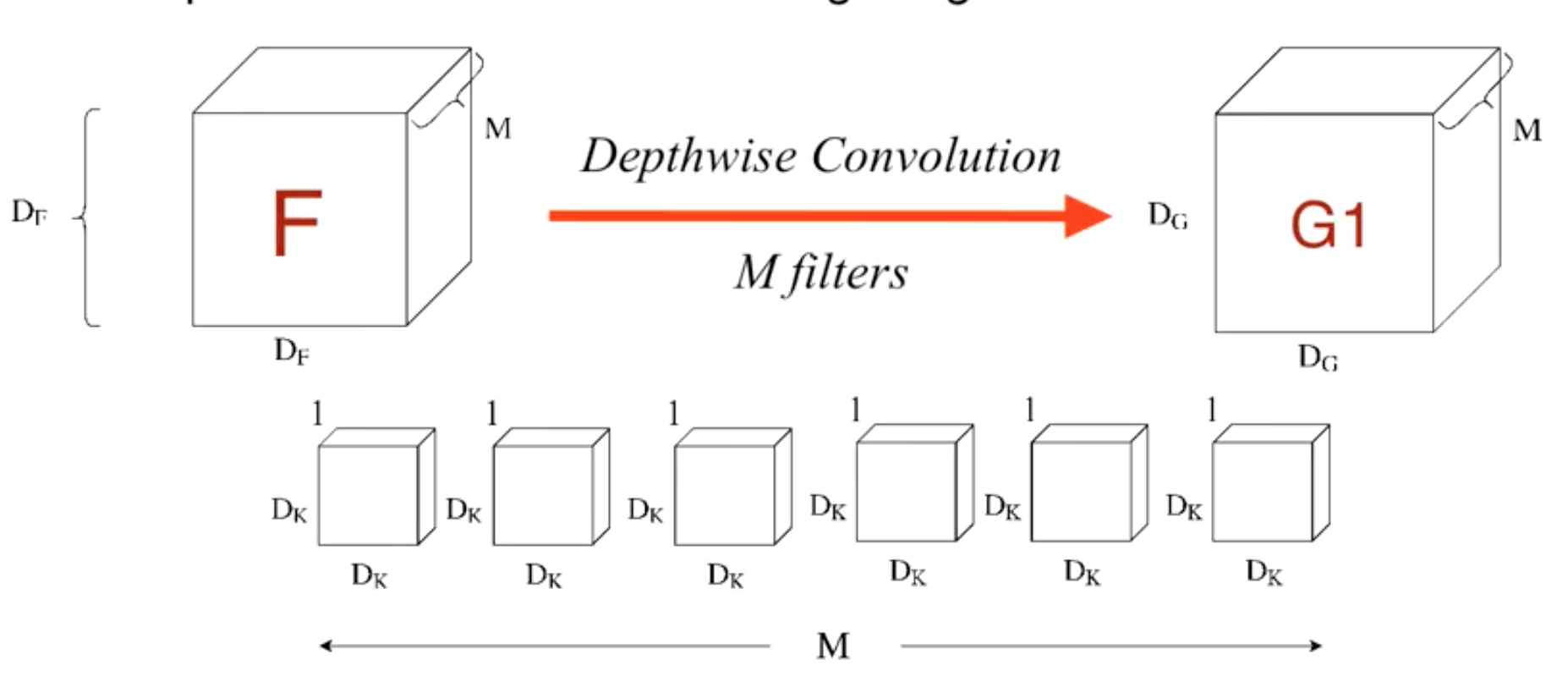
Depthwise convolution. 먼저 채널마다 독립적으로 크기가 $(k, 1)$인 커널(width=$k$, channel size=1)을 사용하여 convolution을 진행하고, 각 채널에서 나온 아웃풋을 stack한다.
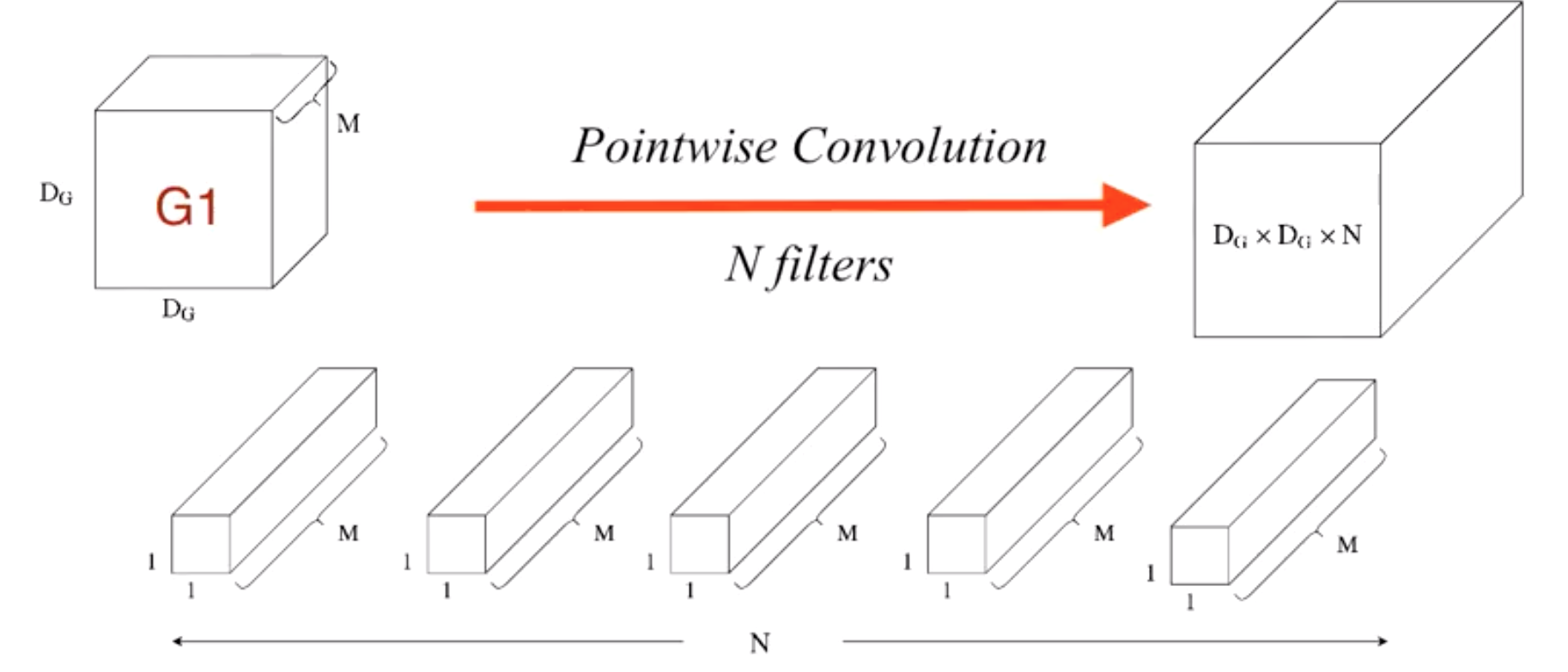
Pointwise convolution. 크기가 (1, $d$)인 커널(width=1, channel size=$d$)을 사용하여 채널들을 합친다.
일반 convolution 대비 계산량을 대폭 줄일 수 있다.
- 일반 conv: $d_{out} \times d_{in} \times g \times k $
- Depthwise conv: $d_{in} \times g \times k$
- Pointwise conv: $d_{out} \times g \times d_{in}$
=> $\frac{DC+PC}{\mathrm{Standard}} = \frac{1}{d_{out}} + \frac{1}{k}$
마찬가지로, parameter 수도 대폭 줄일 수 있다.
- 일반 conv: $d_{out} \times d_{in} \times k$
- Depthwise conv: $d_{in} \times k$
- Pointwise conv: $d_{out} \times d_{in}$
=> $\frac{DC+PC}{\mathrm{Standard}} = \frac{1}{d_{out}} + \frac{1}{k}$
MultiModel Nets, Xception, MobileNets 등에 사용된다. 가벼워서 모바일에 유리하다.
모델
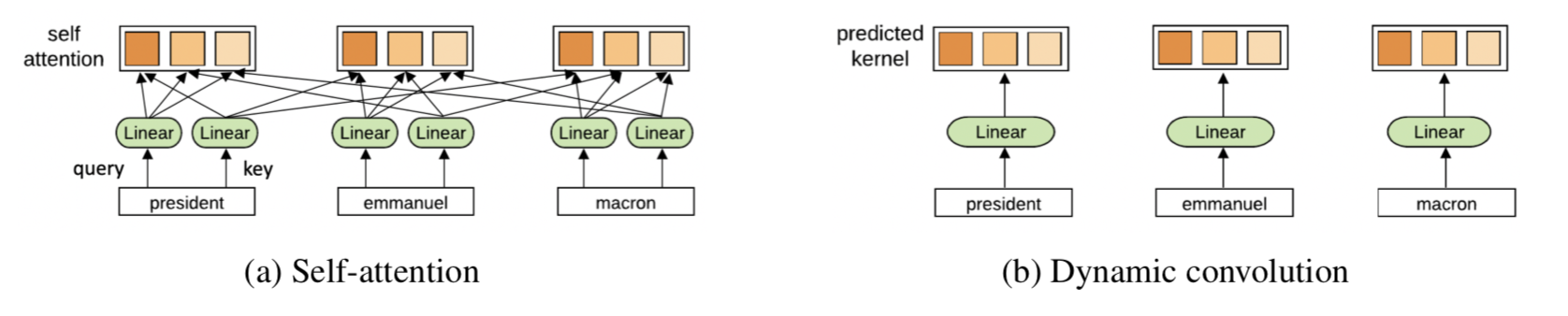
컨텍스트의 내용을 보는 게 아니라 매 타임스텝에서 convolution weight를 학습하는 방식으로, position-based attention이라 할 수 있겠다.
Lightweight convolution
Depthwise convolution의 일종으로, 타임스텝(=position)마다 context element에 할당되는 weight가 달라지지 않는 fixed convolution이다. 커널 width $k$가 fixed context window에 해당된다.
$\mathrm{LightConv}(X, W_{\lceil \frac{cH}{d} \rceil, : :}, i, c) = \mathrm{DepthwiseConv}(X, \mathrm{softmax}(W_{\lceil \frac{cH}{d} \rceil, : :}), i, c)$
Weight sharing (Channel tying). $d$개의 채널 각각이 다른 파라미터를 쓰는 대신, $\frac{d}{H}$ 채널마다 파라미터를 공유하여 수를 줄인다. 즉 채널 $d$개를 $H$개의 블럭으로 나누는 셈이다. 이 경우 파라미터 수는 $\frac{d \times k}{\frac{d}{H}} = H \times k$ 가 된다. 모든 채널을 tie하기도 한다 (H=1).
Softmax-normalization. $W \in \mathbb{R}^{H \times k}$ 의 temporal dimension $(k)$ 에 softmax를 건다. 또한 DropConnect를 regularizer로 사용한다 (채널 내에서 temporal dim의 일부를 제거하는 셈).
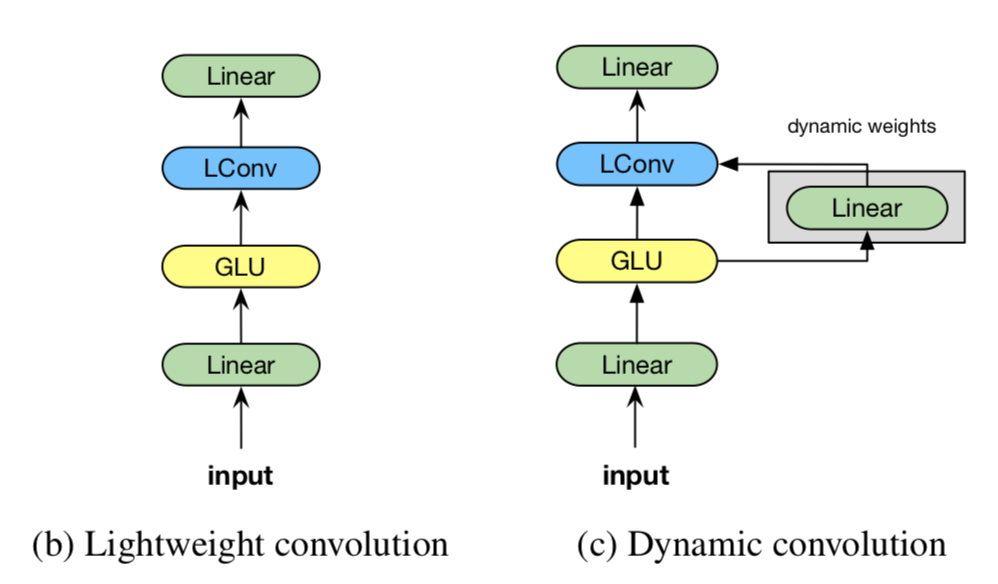
LightConv 레이어는 GLU와 output projection ($d \rightarrow d$) 레이어 사이에 쓰인다. (GLU operation $H=A \times \sigma(B)$ 를 위해 GLU 레이어 전에는 $d \rightarrow 2d$로 project하는 레이어가 필요하다.)
Dynamic convolution
Lightweight convolution의 변형으로, 타임스텝마다 서로 다른 커널을 학습하기 때문에 weight가 달라진다는 점이 다르다. 이러한 dynamic 커널을 배우려면 일반적인 convolution으로는 메모리 부담이 크기 때문에 LightConv를 사용하여 파라미터 수를 줄였다. LightConv의 $W \in \mathbb{R}^{H \times k}$ 이기 때문에, 각 채널을 이 형태로 맵핑하는 함수 $f$ 가 필요하다. 간단하게는 $W^Q \in \mathbb{R}^{H \times k \times d}$의 linear 모듈을 사용할 수 있다.
$\mathrm{DynamicConv}(X, i, c) = \mathrm{LightConv}(X, f(X_i)_{h,:}, i, c) \ \mathrm{where\;\;}f: \mathbb{R}^d \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{H \times k}$
Self-attention과의 비교. 매 타임스텝마다 weight이 달라진다는 점은 같지만, self-attention은 context 전체에 대한 함수인 반면 DynamicConv는 오로지 현재 타임스텝에 대한 함수이다. 따라서 DynamicConv의 커널 계산 복잡도는 $O(N)$이다.
실험
- Tasks: NMT / LM / abstractive summarization.
- 성능: self-attention baseline 대비 모두 개선되거나 비슷
- 레이어당 parameter 감소 (레이어를 늘려서 전체 파라미터 수는 비슷함)
- 런타임 20% 감소
Leave a comment